Anxiety

Anxiety is a feeling of worry, fear, or nervousness that is a natural response to stress or perceived danger. However, when anxiety becomes chronic or excessive, it can interfere with daily life and well-being. Chronic anxiety can lead to several specific anxiety disorders:
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD): Characterized by persistent, excessive worry about various aspects of life, such as health, work, and social interactions. People with GAD often find it difficult to control their anxiety, leading to physical symptoms like fatigue and muscle tension.
Panic Disorder: Involves recurrent, unexpected panic attacks—sudden periods of intense fear or discomfort. During these attacks, individuals may experience symptoms like heart palpitations, shortness of breath, and dizziness. This disorder often leads to fear of future attacks and avoidance of situations where they might occur.
Social Anxiety Disorder: Marked by intense fear of social situations and being judged or embarrassed. This can lead to avoidance of social interactions, which can severely impact relationships and daily functioning.

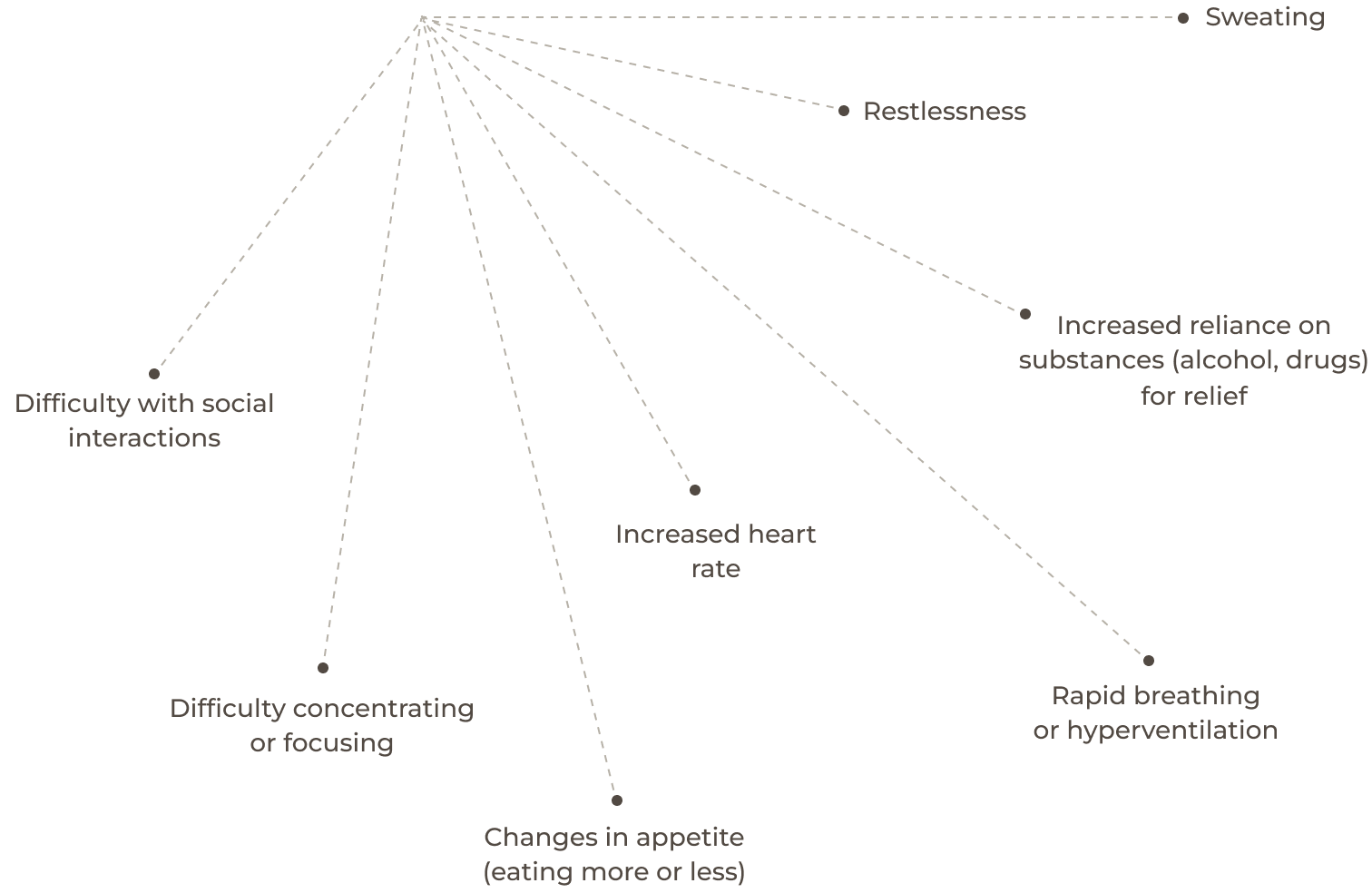
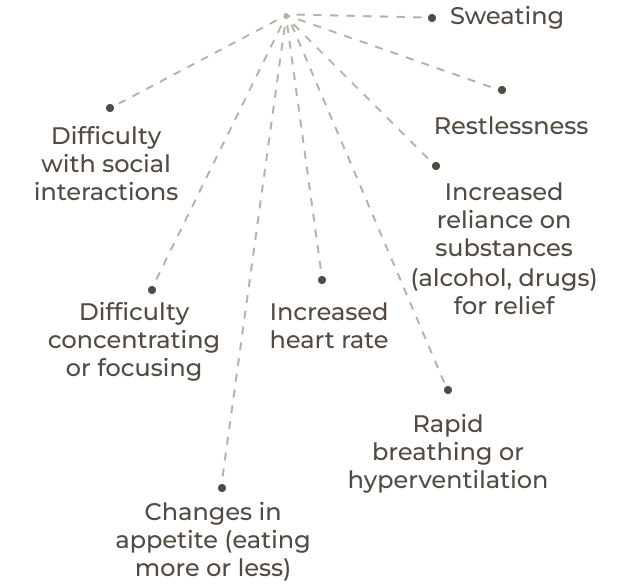
Symptoms
of Anxiety

How We Can Help with Anxiety

During the initial psychiatric evaluation, we conduct a detailed interview to understand the patient’s symptoms, triggers, and impact on daily life. This process allows for accurate diagnosis and differentiation between various anxiety disorders, such as generalized anxiety disorder, panic disorder, and social anxiety disorder. With a clear understanding of the anxiety patient’s situation, we can create a personalized treatment plan that may include medication, therapy options, and coping strategies. This evaluation also provides a supportive atmosphere where patients can express their concerns and feel heard.
For patients facing anxiety, medication management serves as a cornerstone of effective treatment. Based on the comprehensive assessment, providers may prescribe various medications, such as SSRIs for long-term management or benzodiazepines for immediate relief. A comprehensive assessment guides the selection of the most appropriate medication based on the patient’s unique symptoms and medical history. The goal is to create a balanced treatment strategy that addresses both acute and chronic symptoms.
Individual psychotherapy serves as an effective intervention for those experiencing anxiety and provides a personalized exploration of thoughts and emotions. In therapy, we often use techniques such as cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) to help clients identify and modify unhelpful thought patterns that fuel their anxiety. This process equips individuals with practical tools to manage their symptoms, such as relaxation techniques and mindfulness practices. Sessions focus on recognizing triggers, improving emotional responses, and enhancing coping strategies, fostering greater resilience in the face of anxiety.
Laboratory monitoring and psychotropic genetic testing are essential services for patients managing anxiety, as they enhance the precision and safety of treatment. Laboratory monitoring involves regular evaluations to assess how well medications work and to detect any potential side effects early. This proactive approach enables healthcare providers to make timely adjustments to the treatment plan. Psychotropic genetic testing examines an individual’s genetic makeup to understand how they may respond to various medications. By identifying genetic factors that influence drug metabolism, this testing helps tailor medication choices and reduces the likelihood of adverse effects.
Let’s Connect!

